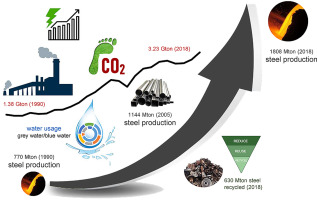
In today’s global economy, environmental sustainability has become a focal point across industries, including steel production. Environmental regulations are increasingly shaping the landscape of steel manufacturing, driving significant changes in operations, technology adoption, and sustainability practices. Let’s delve into how these regulations are transforming the steel production sector and what it means for the industry at large.
The Evolution of Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations governing steel production have evolved significantly over the years, responding to growing concerns about climate change, air quality, and resource conservation. Governments and international bodies have introduced stringent standards to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote energy efficiency, and mitigate environmental impacts associated with steel manufacturing processes.
Impact on Steel Production Processes
- Emission Control and Air Quality Standards
One of the primary focuses of environmental regulations in steel production is the control of emissions, particularly air pollutants such as particulate matter, sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), and carbon dioxide (CO₂). Steel producers are mandated to adopt advanced emission control technologies, including scrubbers, filters, and catalytic converters, to minimize their environmental footprint and comply with emission limits.
Table 1: Compliance with Emission Standards
| Pollutant | Regulatory Limit (per ton of steel) | Compliance Measures |
|---|---|---|
| SO₂ | 50 kg | Installation of scrubbers |
| NOₓ | 100 kg | Use of low-NOₓ burners |
| Particulate Matter | 20 kg | Adoption of filtration systems |
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Resources
To reduce energy consumption and dependency on fossil fuels, steel producers are increasingly adopting energy-efficient technologies and integrating renewable energy sources into their operations. Investments in energy recovery systems, cogeneration facilities, and renewable power generation contribute to sustainable production practices while lowering operational costs over the long term.
- Waste Management and Recycling Initiatives
Environmental regulations encourage steel producers to implement comprehensive waste management strategies, focusing on waste reduction, recycling, and reuse of materials. By minimizing waste generation and maximizing resource recovery, steel manufacturers mitigate environmental impacts and contribute to circular economy principles.
- Water Conservation and Pollution Prevention
Efforts to conserve water resources and prevent water pollution are integral to environmental compliance in steel production. Technologies such as closed-loop water systems, water recycling, and advanced treatment methods help minimize water usage and ensure compliance with stringent water quality standards.
Table 2: Water Conservation Measures
| Water Management Practice | Implementation Impact |
|---|---|
| Closed-loop Water Systems | 30% reduction in water usage |
| Water Recycling Systems | 50% reuse of process water |
| Advanced Treatment Methods | Compliance with discharge limits |
The Path Forward: Embracing Sustainability
In conclusion, environmental regulations are driving a paradigm shift in the steel production industry, pushing manufacturers towards sustainable practices and technological innovation. While compliance presents challenges, it also offers opportunities for growth and differentiation through cleaner production methods and enhanced corporate responsibility.
Steel producers that proactively embrace environmental sustainability not only mitigate regulatory risks but also enhance their reputation, attract environmentally conscious investors, and meet the evolving expectations of customers and stakeholders.
Embrace the journey towards sustainable steel production as a strategic imperative, positioning your organization at the forefront of environmental stewardship and resilience in a rapidly changing world. By aligning with regulatory requirements and adopting best-in-class environmental practices, steel producers can forge a path towards a greener future while driving long-term value and industry leadership.




